Up until now, Synergy Research Corporation’s VisiWork service has supported the introduction and operation of Redmine. However, in our recent user support, we have received many requests not only for the introduction and operation of Redmine, but also for customization of Redmine to solve specific issues that user companies have, or for the development of data integration interfaces between other business systems and Redmine.
Redmine is an open-source software and is available free of charge. Even when using Redmine as a paid SaaS service, the license fee is kept within a reasonable range. Therefore, if Redmine can be used to solve user-specific issues through customization, it is possible to realize very large cost reductions compared to developing everything or using expensive packaged software.
Below we describe in turn four ways to customize Redmine:
| No. | How to Customize Redmine | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Code modification of the main unit | Functional change |
| 2 | Utilizing Custom Fields | Data attribute addition |
| 3 | Development of data linkage function by API (add-in function development) | Data linkage function added |
| 4 | Plug-in Development | Functional expansion |
1. Code modification of the main unit
Redmine is open-source software. When thinking of customizing open-source software, you might imagine obtaining the standard version and modifying the source code. However, this is not commonly done with Redmine.
The specifications of Redmine are managed by redmine.org, and the source code is updated regularly. While users can directly change Redmine’s functionality by modifying the source code, this makes them responsible for keeping up with the standard version updates, which often include security patches. Therefore, changes should be made cautiously.
However, if specific modifications offer significant benefits to a company and there is guaranteed support and budget for maintaining those changes, modifying the standard parts of Redmine can be meaningful. VisiWork services also provide support for such modifications and maintenance.
2. Utilizing custom fields
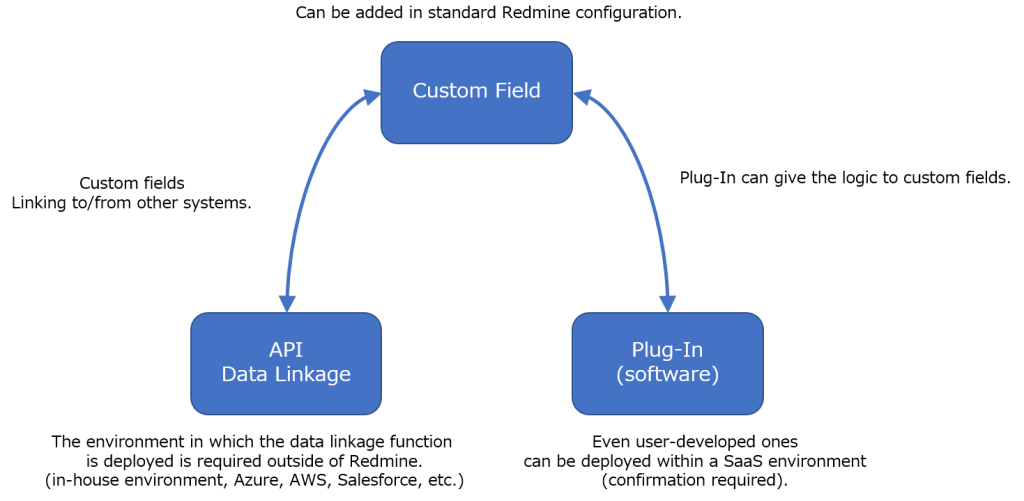
Custom fields are a feature in standard Redmine that allows you to add fields to standard Redmine data, such as tickets, work hours, projects, users, etc., according to user-specific requirements.
Despite the simplicity of this customization method, its ease of use has led most users to use custom fields.
In Table 1 below, the attribute “number of welds” is added as a user-specific requirement for standard tickets.
| No. | Field Name | Data (example) | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | id | 3012 | standard |
| 2 | project | Equipment Projects | |
| 3 | tracker | production | |
| 4 | title | Unit A Production | |
| 5 | status | under inspection | |
| 6 | degree of relative priority | usual | |
| 7 | person in charge | Ichiro Hayashi | |
| 8 | number of welding points | 6 | custom |
3. Development of data linkage function by API
In section 2, we discussed the use of custom fields. What if the data including the number of welding points is stored in an Excel sheet of the person in charge of the design department, and we want to share it with the entire design department using Redmine? The solution to this problem is to develop a data integration function using an API. This is sometimes called add-in or add-on function development.
Standard Redmine has the ability to link data with Excel sheets (CSV format files) using this API, and the data can include custom fields, so custom fields and this method work well together and make standard Redmine a more powerful tool.
However, this standard functionality can be a bit cumbersome to use repeatedly. To solve this problem, VisiWork Service has developed its own tool, TaskBuilder, which is provided free of charge to VisiWork Service customers (see related article).
However, when performing such data linkage as a routine task, it is ideal to improve efficiency by developing data linkage functions using APIs to fully automate the process and execute it on a regular basis.
4. Plug-in Development
Plug-in development is the mainstay of user-specific problem-solving methods. Plug-in development allows users to implement their own specifications without changing the standard code.
This will allow you to add your own screens, data, and logic, avoiding the problems that arise from modifying the standard Redmine source code, as pointed out in section 1.
By developing a plugin, it is possible to introduce the custom fields described in section 2. and then provide your own calculation logic for those custom fields.
For example, you can add ticket attributes such as the number of welds, length, width, and height of the product to be manufactured, as well as the number of scheduled man-hours, which is the basic information for scheduling, to be automatically calculated. It is also possible to prevent users from directly updating the scheduled man-hours to an arbitrary value using the standard ticket screen by properly setting the “Permissions on workflow fields” in the Redmine settings.
It is also important to note that such plug-ins, even if developed individually by the user, can usually be deployed in SaaS.
Of the four methods described above, except for 1. modifying the source code directly, the other three methods can be actively used to create a customized Redmine that solves user-specific issues.
The relationship and description of these three methods is shown in Figure 2.
For inquiries about this article, please send them to our Contact page.

